What You Will Learn in a Basic First Aid Course
Introduction
A basic first aid course is a fundamental step toward being prepared to handle emergencies effectively. These courses provide essential knowledge and skills that can be crucial in various situations, from everyday accidents to critical emergencies. This article explores the core components of a basic first aid course, detailing what you will learn and how this training can make a significant difference in your ability to respond to medical incidents.
Understanding First Aid Fundamentals
1. Definition and Principles of First Aid
A basic first aid course starts with an overview of what first aid is and its fundamental principles. First aid involves providing immediate care to someone who is injured or ill until professional medical help arrives. The principles taught include:
Preserving Life: Ensuring that the injured or ill person’s life is preserved.
Preventing Further Harm: Taking steps to prevent the situation from worsening.
Promoting Recovery: Providing care that helps in the healing process.
2. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Understanding the legal and ethical aspects of first aid is crucial. This includes knowing:
Consent: How to obtain consent from the injured person before providing aid.
Duty of Care: Understanding your responsibilities and limitations when providing first aid.
Legal Protection: Awareness of legal protections and potential liabilities associated with first aid.
Basic Life Support Techniques
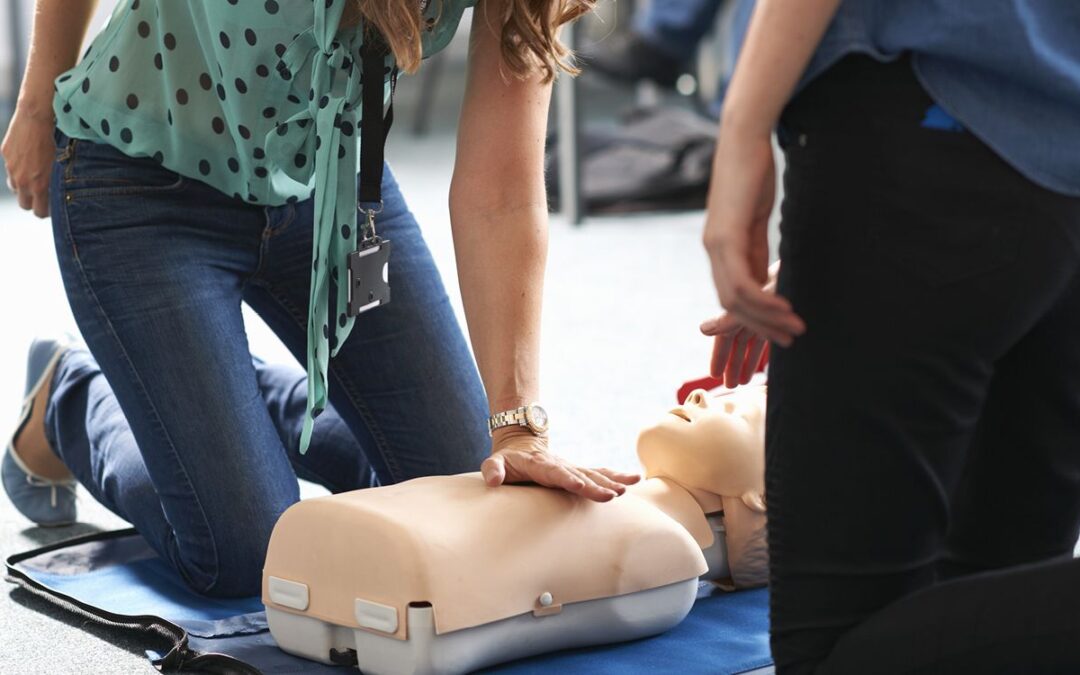
1. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
CPR is a critical component of basic first aid training. The course covers:
Recognizing Cardiac Arrest: Identifying signs of cardiac arrest and when to perform CPR.
Performing Chest Compressions: Proper technique and depth for chest compressions.
Giving Rescue Breaths: How to provide effective rescue breaths to assist with breathing.
2. Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Use
Basic first aid courses often include training on using an AED, which involves:
Understanding AED Functionality: How AEDs work and their role in cardiac emergencies.
Proper AED Usage: Steps for applying AED pads and following device prompts to deliver a shock if needed.
3. Recovery Position
Learning how to place someone in the recovery position is essential for:
Maintaining Open Airway: Ensuring that the person’s airway remains clear.
Preventing Choking: Reducing the risk of choking on vomit or fluids.
Managing Common Injuries and Illnesses
1. Wound Care and Bleeding Control
The course teaches you how to handle various types of wounds and bleeding, including:
Cleaning and Dressing Wounds: Techniques for cleaning wounds and applying dressings to prevent infection.
Controlling Bleeding: Methods for applying pressure, using bandages, and elevating limbs to manage bleeding.
2. Treating Burns
You will learn how to manage burns, including:
Cooling Burns: Applying cool water to burns to reduce pain and damage.
Covering Burns: Using sterile dressings and avoiding common mistakes like using ointments.
3. Recognizing and Responding to Shock
The course covers signs of shock and how to respond, including:
Symptoms of Shock: Identifying signs such as pale skin, rapid breathing, and confusion.
Managing Shock: Techniques for positioning the person, maintaining body temperature, and providing reassurance.
Responding to Medical Emergencies
1. Choking Emergencies
Learning how to handle choking emergencies involves:
Recognizing Choking: Signs that someone is choking and cannot breathe.
Performing Heimlich Maneuver: Techniques for administering abdominal thrusts to expel an obstruction.
2. Recognizing and Treating Allergic Reactions
The course includes information on managing allergic reactions, including:
Identifying Severe Allergic Reactions: Symptoms of anaphylaxis, such as swelling and difficulty breathing.
Using EpiPens: Proper use of epinephrine auto-injectors for severe allergic reactions.
3. Managing Seizures
You will learn how to respond to seizures, including:
Understanding Seizure Types: Recognizing different types of seizures and their symptoms.
Providing Safe Care: Ensuring safety during a seizure and what to do afterward.
Special Considerations
1. First Aid for Children and Infants
Basic first aid courses often include specific training for handling emergencies involving children and infants:
Differences in Techniques: Adapting techniques for smaller bodies and different developmental stages.
Common Pediatric Emergencies: Addressing issues like choking, fever, and falls.
2. First Aid in Different Environments
Training may cover first aid considerations in various settings, such as:
Workplace First Aid: Handling injuries common in specific work environments.
Outdoor and Remote Areas: Adapting first aid techniques for situations where professional help may be delayed.
Practical Skills and Hands-On Training
1. Simulations and Role-Playing
Basic first aid courses include practical exercises and role-playing scenarios to:
Practice Techniques: Apply learned skills in simulated emergency situations.
Build Confidence: Gain hands-on experience to enhance your response in real-life situations.
2. Skills Assessment
Courses often include assessments to:
Evaluate Competency: Demonstrate your ability to perform first aid techniques correctly.
Receive Feedback: Get guidance on improving your skills and addressing any weaknesses.
Conclusion
A basic first aid course provides essential training that equips you with the skills and knowledge needed to respond effectively to emergencies. From fundamental principles and basic life support techniques to managing common injuries and medical emergencies, this training prepares you to handle a wide range of situations. By participating in a basic first aid course, you not only gain valuable life-saving skills but also contribute to creating a safer environment for yourself and those around you.