
by Mehedi Hasaan | Mar 24, 2025 | blog
Why Every Used Car Buyer in Melbourne Needs a Mobile Pre-Purchase Inspection
Buying a used car in Melbourne can be an exciting step, but it also comes with risks. Hidden mechanical issues, undisclosed damage, and overpriced listings are all too common in the local market. That’s why an increasing number of smart buyers are choosing mobile pre purchase car inspections in Melbourne before making a decision.
Instead of relying solely on what the seller tells you, a professional inspection gives you clear, unbiased information about the vehicle’s true condition. With services like Instant Auto Reach, certified mechanics come directly to your chosen location saving time, money, and plenty of stress.
The Hidden Risks of Buying Without an Inspection
When purchasing a second-hand car, it’s easy to overlook problems that aren’t visible during a quick test drive. Some of the most common risks include:
- Engine wear and transmission problems.
- Structural or accident damage that has been poorly repaired.
- Electrical issues that only show up later.
- Overpaying for a vehicle that isn’t worth the asking price.
A thorough pre-purchase car inspection in Melbourne prevents these costly mistakes by highlighting the real condition of the car before you commit.
What a Mobile Car Inspection Includes
Professional services like Instant Auto Reach provide a detailed checklist covering more than 200 points. This typically includes:
- Full mechanical and electrical checks.
- Suspension, brakes, and steering assessment.
- Body condition and paintwork evaluation.
- Diagnostic scans and test drives.
- Same-day photo and video reports.
For anyone comparing used cars in Melbourne, these detailed reports are essential for negotiating fairlyor walking away if the deal isn’t right.
Services That Match Different Needs
Not all buyers are the same, so having tailored options is key. That’s why services like Instant Auto Reach inspection packages include:
- Standard pre-purchase inspections.
- End-of-warranty checks.
- Fleet and commercial vehicle inspections.
- Luxury and performance car evaluations.
No matter what you’re buying, these inspections provide peace of mind and clarity before you hand over the money.
Melbourne-Wide Coverage
One of the biggest advantages is that inspections are offered across the city and surrounding suburbs. For example:
- In Hastings, buyers get in-depth local inspections tailored to the Mornington Peninsula market.
- Around Brunswick, fast mobile checks are ideal for busy inner-city professionals.
- In Reservoir, detailed reports help families secure safe and reliable vehicles.
Wherever you’re located, a mobile inspection ensures convenience without sacrificing quality.
Why Mobile Inspections Are the Smart Choice
Opting for a mobile car inspection in Melbourne makes sense for several reasons:
- Convenience – No need to drive to a workshop.
- Time savings – Same-day reports delivered directly to your inbox.
- Better negotiation – Evidence-based reports to support your offer.
- Cost-effective – A small upfront cost can save thousands in future repairs.
How to Book a Mobile Inspection
The process is straightforward:
- Visit the Instant Auto Reach.
- Choose the right inspection service.
- Enter your location in Melbourne.
- Confirm the time and date.
- Meet the mechanic at your chosen site.
- Receive your detailed digital report the same day.
This simple system makes it easy to buy with confidence.
Real-Life Scenarios from Melbourne Buyers
- A student in Brunswick avoids an unreliable car thanks to an inspection that uncovered hidden transmission issues.
- A family in Reservoir secures a safe first car for their teenager.
- A collector in Hastings confirms the authenticity of a classic model before purchase.
These examples show how inspections save buyers from financial losses and safety risks.
Conclusion
Used cars can be a smart investment, but only if you know what you’re buying. By booking a mobile pre purchase inspection in Melbourne, you gain valuable insight into the car’s condition before handing over your hard-earned money.
For peace of mind across Melbourne whether in Hastings, Brunswick, or Reservoir services like Instant Auto Reach make buying a car simple, transparent, and stress-free.

by admin | Dec 4, 2024 | blog
Why Take a First Aid Course?
Accidents can happen at any time, whether at work, home, or in public spaces. Being prepared for emergencies is crucial, and one of the most important skills anyone can have is the ability to provide first aid. A first aid course equips individuals with the knowledge and confidence to manage emergencies and provide immediate care before professional medical help arrives. In this article, we explore the many reasons why taking a first aid course is a smart decision, both for personal safety and the well-being of others.
1. Immediate Response in Emergency Situations
When an accident or medical emergency occurs, every second counts. Immediate action can be the difference between life and death, or between a minor injury and something more serious. A first aid course prepares you to respond quickly and effectively, providing the best chance for a positive outcome.
Key Emergency Scenarios Covered
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation): A fundamental aspect of first aid training is learning how to perform CPR, a life-saving technique used when someone’s heart stops beating.
Choking: Knowing how to help someone who is choking can prevent serious injury or even death.
Bleeding and Wounds: First aid courses teach how to stop bleeding and manage wounds, which is critical in preventing infection or further complications.
Fractures and Sprains: First aid training covers how to immobilize fractures and manage sprains until medical help arrives.
By being trained in first aid, you can take immediate action to stabilize someone’s condition and minimize the impact of their injury or illness until professional help arrives.
2. Building Confidence in Handling Medical Emergencies
Many people feel unsure or anxious when faced with a medical emergency, unsure of how to react or what steps to take. A first aid course builds confidence by teaching practical, hands-on techniques for managing a wide range of medical situations. The more you practice these techniques, the more confident you become in your ability to respond when needed.
How First Aid Training Boosts Confidence
Real-World Simulations: First aid courses often include practical exercises and simulations that mirror real-life emergencies, giving you the opportunity to practice your skills in a safe environment.
Clear, Step-by-Step Instructions: First aid courses break down complex medical procedures into simple steps, making it easier for anyone to learn and apply the techniques effectively.
Expert Guidance: Training is typically provided by experienced professionals who offer guidance, tips, and feedback, helping you feel confident in your abilities.
With the knowledge gained from a first aid course, you’ll be able to step in during an emergency with the assurance that you’re equipped to help.
3. Saving Lives and Reducing the Severity of Injuries
One of the most compelling reasons to take a first aid course is the potential to save lives. In emergencies such as cardiac arrest, choking, or severe bleeding, quick and effective first aid can significantly improve a person’s chances of survival and recovery. Being trained in first aid enables you to perform critical interventions that can make a life-saving difference.

Why Take a First Aid Course?
Cardiac Arrest Response: In the case of sudden cardiac arrest, performing CPR immediately can double or even triple a person’s chance of survival.
Preventing Shock: For those suffering from severe trauma or blood loss, first aid can help prevent shock, a potentially life-threatening condition that can result from untreated injuries.
Breathing and Circulation Support: First aid training includes how to maintain breathing and circulation until emergency medical services (EMS) arrive, which is crucial in sustaining life.
By taking a first aid course, you’ll gain the ability to help in life-or-death situations, potentially saving someone’s life or reducing the severity of their injuries.
4. Providing Help Until Professional Medical Assistance Arrives
While waiting for emergency medical services to arrive, the injured or ill person may need care to prevent their condition from worsening. First aid training gives you the skills to offer the necessary support and maintain the person’s condition until professional help arrives.
Supporting Someone Before EMS Arrives
Managing Airway Obstructions: You’ll learn how to help someone who is having difficulty breathing or has an obstructed airway.
Stabilizing a Person: In the case of fractures, sprains, or head injuries, you’ll be trained to stabilize the person’s condition and prevent further harm until EMS arrives.
Emotional Support: First aid training also covers how to offer reassurance and calm an injured person, which can be just as important in maintaining their mental state until professional help arrives.
Even if you’re not the one delivering full medical treatment, your intervention can play a key role in preserving life and preventing further harm.
5. Enhancing Workplace Safety
In many workplaces, safety is a top priority. A first aid course can be especially valuable for employees, as it enables them to handle potential medical emergencies within the work environment. Whether you work in an office, a factory, or a healthcare setting, having employees trained in first aid ensures that your workplace is safer and that help is readily available in case of an emergency.
Workplace Safety and First Aid
Compliance with Regulations: In many industries, employers are required to have first aid-trained personnel to comply with health and safety regulations.
Quick Response to Accidents: Workplaces that have first aid-trained employees can respond quickly to accidents, reducing the potential severity of injuries.
Improved Morale: Employees who know that their colleagues are trained in first aid can feel more secure and supported, which improves morale and creates a safer work environment.
First aid training is an investment in the overall safety of the workplace, ensuring that everyone is prepared to handle emergencies when they arise.
6. Better Preparedness for Family and Friends
Emergencies don’t only happen at work or in public places—they can also occur at home, among family and friends. Having first aid training can make you more prepared to handle medical situations involving loved ones. Whether it’s a child, elderly relative, or even a neighbor, you can offer help when they need it most.
Family and Community First Aid Preparedness
Handling Common Injuries at Home: You’ll be trained to deal with common household injuries such as burns, cuts, and falls.
Childcare First Aid: First aid courses also include techniques specific to children and infants, such as how to handle choking or allergic reactions.
Emergency Situations in Public: Being prepared to respond to emergencies outside of your home—whether in public spaces or at social events—helps you provide assistance to others in need.
By learning first aid, you become a valuable resource for your family and community, ensuring that those around you receive immediate care when necessary.
7. Boosting Personal Safety and Awareness
Learning first aid isn’t just about being able to help others; it also boosts your own personal safety awareness. Understanding how to recognize the signs of a medical emergency, such as a heart attack or stroke, can make you more vigilant in protecting your own health and well-being. https://aimsinstitute.edu.au/first-aid-cpr/
Personal Safety Awareness Benefits
Recognizing Warning Signs: First aid training helps you learn to recognize early warning signs of medical conditions like heart attacks, strokes, and seizures, allowing you to seek help early.
Preventing Accidents: Knowing basic first aid can help you identify hazards in your environment, which may prevent accidents or injuries from occurring in the first place.
Self-Care: First aid courses often cover self-care techniques, such as how to treat minor injuries and prevent infection.
By learning first aid, you not only become a better caregiver to others but also develop a heightened awareness of your own health and safety.
8. Making a Positive Impact on Your Community
Taking a first aid course can also have a broader impact on your community. When more people are trained in first aid, the entire community becomes safer. Whether you are volunteering at an event, working in a public space, or simply spending time in your neighborhood, your ability to provide first aid can help those in need and potentially save lives.
Community Impact of First Aid Training
Community Volunteering: Many community programs and events benefit from volunteers who are trained in first aid, providing support to others in case of emergencies.
Public Health Initiatives: Public health initiatives often require first aid-trained individuals to offer support in case of medical emergencies.
Encouraging Others to Get Trained: By setting an example, you can encourage others in your community to take first aid courses, further enhancing the safety and preparedness of the area.
Becoming first aid-certified can give you the skills and confidence to make a difference in your community, ensuring that help is always available when needed.
Conclusion
Taking a first aid course offers a wide range of benefits, from enhancing personal confidence to saving lives in emergencies. Whether you’re looking to be prepared in the workplace, at home, or in the community, first aid training equips you with the skills to respond effectively to a variety of medical situations. By gaining this invaluable knowledge, you become an asset to those around you, helping to create a safer, more supportive environment wherever you are.

by admin | Dec 3, 2024 | blog
Career Benefits of Work Health and Safety Training
Work Health and Safety (WHS) training is an essential investment for both individuals and organizations. In today’s competitive job market, professionals who are trained in workplace safety stand out to employers and can make significant advancements in their careers. This article highlights the various career benefits of completing WHS training, showing how this qualification can enhance job opportunities, boost skills, and lead to long-term career growth.
1. Enhanced Employability and Job Opportunities
In any industry, safety is a priority, and employers highly value individuals who understand workplace health and safety protocols. Completing WHS training demonstrates to potential employers that you are serious about maintaining a safe work environment and have the knowledge to prevent workplace accidents. This can make you more employable, as many organizations require their staff to have basic WHS knowledge.
How WHS Training Enhances Employability
Attracting Employers’ Attention: WHS training shows employers that you understand the importance of safety, which is crucial in many sectors such as construction, manufacturing, healthcare, and more.
Meeting Job Requirements: Some industries, particularly those with high-risk environments, mandate that employees complete WHS training. Having this certification can make you eligible for jobs that require safety knowledge.
Industry-Specific Roles: Many industries such as mining, healthcare, and engineering place a strong emphasis on safety. A WHS qualification is often required for roles in these sectors, ensuring your eligibility for various positions.
WHS training not only makes you more attractive to potential employers but also opens doors to specialized roles that prioritize safety and health compliance.
2. Career Advancement and Professional Growth
For individuals already in the workforce, completing WHS training can lead to career advancement. Organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of having staff members who are trained to handle safety issues. Employees with WHS training are more likely to be considered for promotions or higher-level roles, such as safety officers, supervisors, or managers. The ability to ensure a safe work environment can also give you a leadership edge within your organization.
Career Progression through WHS Training
Leadership Roles in Safety Management: Having WHS training qualifies you to take on roles such as Safety Officer, Health and Safety Coordinator, or Occupational Health and Safety Manager. These positions come with increased responsibility and higher salaries.
Increased Responsibilities: Employees with WHS knowledge are often entrusted with more critical roles in managing workplace health and safety, allowing for greater career responsibilities and leadership opportunities.
Wider Job Opportunities: Completing WHS training opens the door to more job positions, not only within your current company but across various organizations that prioritize safety.
WHS training can provide the stepping stones to climb the career ladder, especially in industries where safety is a major concern. See our articles here.
3. Increased Job Security
Employees who are trained in workplace safety are seen as valuable assets to their employers. When you have WHS training, employers are more likely to recognize your contribution to creating a safer workplace, leading to greater job security. A safe work environment reduces the likelihood of workplace accidents, which can be costly in terms of both finances and reputation.

Career Benefits of Work Health and Safety Training
Reduced Risk of Accidents: Having the proper safety knowledge minimizes the chances of workplace accidents and the potential for lawsuits or insurance claims. This helps organizations maintain a safe reputation and ensures job stability for their employees.
Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are highly regulated when it comes to health and safety standards. Employers who invest in staff WHS training ensure that they comply with these regulations, preventing potential legal issues that could affect employee job security.
Proactive Safety Measures: Employers who prioritize safety are less likely to experience injuries, work disruptions, and costly compensation claims, which indirectly protect employees’ positions within the company.
The ability to prevent and manage safety issues in the workplace directly contributes to the overall stability and longevity of your career.
4. Competitive Advantage in the Job Market
In today’s competitive job market, candidates with additional certifications or specialized training have an advantage over others. Completing WHS training gives you a competitive edge, demonstrating your commitment to safety and making you stand out from other candidates applying for similar positions. For roles that require WHS knowledge, having this certification can be the difference between securing the job and being passed over.
Why WHS Training Gives You a Competitive Advantage
In-Demand Skillset: WHS knowledge is sought after in many industries, and being trained in safety procedures shows that you are prepared for the job. It can set you apart from other job seekers who lack this qualification.
Proactive and Responsible Employee: Employers appreciate employees who proactively seek out training and take responsibility for their own safety education. This shows initiative and the willingness to contribute to a positive work environment.
Preferred Candidate for High-Risk Roles: Many high-risk industries, such as construction and manufacturing, value candidates with WHS training more highly, as they can help mitigate risks and ensure safety protocols are followed.
By showcasing your WHS qualifications, you improve your chances of securing your ideal job or gaining an advantage in the hiring process.
5. Salary Potential and Financial Benefits
In addition to enhancing employability, WHS training can increase your earning potential. Employers are often willing to pay more for employees who have the knowledge and skills to maintain a safe workplace. Roles such as Health and Safety Officer or Safety Manager often come with higher salaries and more benefits due to the specialized nature of the job.
How WHS Training Can Increase Earnings
Specialized Roles with Higher Pay: Employees who are responsible for health and safety compliance typically receive higher wages due to the specialized skill set required for these positions.
Negotiation Power: Having WHS training can strengthen your position when negotiating salary increases or job offers, as it provides employers with confidence in your ability to manage workplace safety.
Career Longevity and Benefits: Specialized WHS roles often come with additional perks such as bonuses, insurance, or even company-provided equipment, adding to your overall financial compensation.
Investing in WHS training can have significant long-term financial benefits, both through higher salaries and additional job benefits.
6. Development of Transferable Skills
One of the key advantages of WHS training is the development of transferable skills that can be used in many different roles and industries. Beyond just safety management, WHS courses often cover skills such as risk assessment, communication, problem-solving, and leadership, which can be applied to a wide range of job functions.
Transferable Skills Gained from WHS Training
Risk Assessment and Management: The ability to identify, assess, and control risks is valuable not only in safety roles but also in project management, operations, and logistics.
Communication Skills: WHS training emphasizes the importance of clear communication, especially during emergencies. This skill is crucial in roles that require teamwork, customer service, or management.
Leadership and Decision-Making: Many WHS courses teach leadership skills, which are beneficial for those seeking management or supervisory roles. Being able to make informed decisions quickly is a key skill for career progression.
Problem-Solving: A key aspect of WHS training is learning how to handle unexpected safety issues. These problem-solving skills are valuable in nearly any career, particularly in high-pressure environments.
The wide range of skills developed through WHS training makes it a valuable qualification, even for those who wish to transition to different roles or industries in the future.
7. Contribution to a Safer Work Environment
Finally, one of the most rewarding aspects of completing WHS training is the opportunity to make a positive impact on workplace culture. A safer environment benefits everyone: employees, management, and clients. By contributing to the creation of a safer workplace, you not only protect your own well-being but also help safeguard your colleagues, which can lead to higher job satisfaction and overall career fulfillment.
Making a Positive Impact
Fostering a Culture of Safety: WHS training allows you to play an active role in promoting safety and well-being within the organization, which can lead to a more positive and productive work environment.
Boosting Team Morale: When employees feel safe, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated in their work. As a result, you can help improve team morale and workplace culture.
Preventing Workplace Incidents: By applying the safety knowledge gained from WHS training, you contribute to reducing workplace accidents, enhancing productivity, and ensuring that everyone remains safe.
By actively promoting and participating in safety initiatives, you contribute to a work environment that prioritizes the well-being of all employees.
Conclusion
Work Health and Safety training offers numerous career benefits, from enhancing employability to increasing earning potential. Whether you’re entering the workforce or looking to advance within your current job, WHS training equips you with the skills and knowledge necessary to make a positive impact on your career and workplace. With higher job security, improved career prospects, and the development of valuable transferable skills, completing WHS training is a wise investment that can pay off in numerous ways throughout your professional life. Find our white card course here.

by admin | Dec 3, 2024 | blog
Benefits of a Work Health and Safety Course
Workplace safety is a top priority for businesses worldwide. Ensuring that employees are not only productive but also safe in their work environment is essential for the success and sustainability of any organization. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is through proper training, and a Work Health and Safety (WHS) course is a key part of that strategy. This article outlines the various benefits of completing a WHS course, both for individuals and organizations.
The primary benefit of completing a Work Health and Safety course is the improvement in workplace safety. By understanding the legal requirements and best practices surrounding workplace safety, employees can significantly reduce the risks of accidents, injuries, and illnesses. A WHS course provides essential knowledge about how to identify hazards, assess risks, and implement control measures to prevent accidents.
Key Safety Practices Learned
Risk Assessment: Identifying and evaluating potential hazards in the workplace.
Hazard Control: Learning how to control and minimize risks to protect employees.
Emergency Procedures: Knowing how to act during an emergency, including first aid, evacuation plans, and how to use safety equipment properly.
Health and Safety Legislation: Understanding the laws and regulations that govern workplace safety, ensuring compliance.
By providing this knowledge, a WHS course ensures that employees are well-equipped to handle potential risks and maintain a safe environment for everyone.
2. Legal Compliance and Reduced Liability
Workplace health and safety laws are not just guidelines—they are legally binding regulations. Employers have a legal responsibility to ensure the health and safety of their employees, and failing to comply with safety laws can result in fines, penalties, or even legal action. Completing a WHS course ensures that employees are aware of their rights and responsibilities when it comes to workplace safety, thus helping organizations maintain compliance with the law.
Legal Benefits for Employers
Avoiding Legal Penalties: Businesses that fail to comply with workplace safety regulations face hefty fines and penalties. WHS training ensures compliance and reduces the risk of violations.
Insurance Premium Reduction: By fostering a safer workplace, companies may reduce their insurance premiums since the risk of workplace accidents and related claims is minimized.
Liability Protection: Employers who invest in WHS training demonstrate due diligence in protecting their employees, which can be important in the event of a workplace accident or legal dispute.
For employers, a WHS course is an investment in the legal protection of their business, as well as the well-being of their workforce.
3. Enhanced Employee Morale and Productivity
When employees feel safe and valued in their workplace, they are more likely to be motivated, engaged, and productive. Completing a WHS course equips employees with the confidence that their well-being is a top priority for the company. This sense of security fosters a positive workplace culture, leading to higher employee morale and job satisfaction.
How WHS Training Improves Workplace Environment
Increased Job Satisfaction: Employees who feel safe and protected are more likely to enjoy their work environment and feel more secure in their roles.
Boosted Employee Engagement: Safety-conscious employees are more likely to be engaged with their work, as they understand that their well-being is a priority for the organization.
Reduced Absenteeism: By preventing workplace injuries and illnesses, WHS training leads to fewer days off due to injury or illness, thus improving overall productivity.

Benefits of a Work Health and Safety Course
In a workplace where safety is prioritized, employees are more focused, motivated, and dedicated to their tasks, which in turn increases the overall productivity of the business.
4. Cost Savings for Employers
Workplace injuries and illnesses are costly. Medical bills, compensation claims, legal fees, and the costs of training replacement staff add up quickly. One of the most significant benefits of a WHS course is its potential to reduce these costs. By preventing accidents and promoting a safer workplace, companies can lower their overall operational costs. Find our different courses here.
Financial Advantages for Employers
Lower Workers’ Compensation Costs: Fewer workplace injuries mean fewer compensation claims, which can lead to lower insurance premiums.
Reduced Medical Expenses: Fewer accidents mean fewer medical bills and less time spent on treating injuries.
Minimized Disruption: Accidents can disrupt daily operations, leading to delays or even shutdowns. A safer workplace minimizes these disruptions, ensuring smoother operations.
By investing in a WHS course, employers can reduce the financial burden caused by workplace accidents, improving the bottom line.
5. Career Advancement Opportunities
For individuals, completing a Work Health and Safety course can lead to better career prospects. Having a formal qualification in workplace safety is highly regarded by employers in various industries, and it can give candidates an edge in competitive job markets. Whether you’re looking to move into a safety management role or simply want to demonstrate your commitment to creating a safe work environment, a WHS course can be a valuable addition to your skill set.
Career Benefits for Employees
Increased Employability: WHS certification can make you more attractive to potential employers who are looking for safety-conscious professionals.
Career Progression: Many industries value health and safety knowledge and may offer career progression opportunities for those with relevant qualifications.
Skill Development: In addition to technical safety skills, a WHS course also enhances communication, leadership, and problem-solving abilities, which are essential for career growth.
By acquiring a WHS qualification, employees can position themselves for new roles and career advancement within organizations that prioritize safety. Find our work health and safety course here.
6. Promotes a Culture of Safety within the Organization
Implementing a comprehensive Work Health and Safety program is an excellent way to foster a safety-conscious culture within an organization. By investing in WHS training for employees, companies signal that they are committed to creating a safe and healthy environment for all. This proactive approach not only benefits employees but also improves the organization’s overall safety culture, which can lead to long-term success.
Building a Safety-Oriented Workplace Culture
Leadership in Safety: Employees who receive WHS training are more likely to be proactive in identifying hazards and reporting risks, leading by example for others.
Encouraging Safe Behavior: A WHS course helps instill the importance of safety in all employees, encouraging them to make safety-conscious decisions in their daily tasks.
Promoting Teamwork: Safety training often involves teamwork and collaboration, which fosters a collective sense of responsibility for maintaining a safe workplace.
A strong culture of safety not only protects employees but also enhances organizational reputation and performance.
7. Confidence in Managing Workplace Emergencies
Accidents and emergencies can occur at any time, but the difference between a minor incident and a major disaster often lies in how well employees respond. A WHS course provides employees with the knowledge and practical skills to handle emergencies effectively, such as fire evacuations, first aid, and other critical situations.
Emergency Management Skills
First Aid Training: Many WHS courses include first aid training, teaching employees how to administer basic medical care in case of an emergency.
Evacuation Procedures: Employees learn how to safely evacuate a building and help others during an emergency situation.
Crisis Communication: Understanding how to communicate during a crisis is crucial, and WHS training ensures that employees are equipped to relay important information during emergencies.
By providing employees with the necessary emergency management skills, a WHS course ensures that workplaces can handle unforeseen situations with confidence, minimizing the impact of accidents or disasters.
Conclusion
A Work Health and Safety course offers a wide range of benefits, both for employees and employers. From improving workplace safety and legal compliance to reducing costs and boosting productivity, the advantages of completing a WHS course are clear. Furthermore, the course helps build a culture of safety, promotes career advancement, and ensures employees are well-prepared to handle emergencies. For anyone looking to enhance their professional qualifications and contribute to a safer workplace, a WHS course is an invaluable investment. https://www.breakthrucollege.edu.au/qualifications/certificate-iv-in-disability/

by admin | Dec 2, 2024 | blog
The business world is dynamic, and staying competitive often means upgrading your skills and qualifications. For many individuals aiming to fast-track their careers or enhance their professional expertise, completing a Diploma of Business is a highly valuable investment. This qualification not only opens up numerous career opportunities but also equips individuals with the skills to excel in a variety of roles across industries. In this article, we will explore the top benefits of completing a Diploma of Business.
1. Enhances Professional Skills
A Diploma of Business provides a comprehensive foundation in key areas of business, such as management, marketing, finance, human resources, and operations. The coursework is designed to give students practical skills that are directly applicable to real-world business settings. By completing the diploma, individuals learn to manage and lead teams, handle budgets, develop marketing strategies, and effectively communicate with various stakeholders. These are all skills that can set someone apart in the competitive job market.
Key Skills Developed
Leadership and management: Understanding how to lead a team and make critical business decisions is one of the core components of the diploma.
Project management: Students learn how to manage projects, allocate resources, and meet deadlines efficiently.
Communication and negotiation: Effective communication is crucial in any business environment, and the diploma hones verbal and written communication skills.
Problem-solving and decision-making: Students are trained to analyze business situations and make informed decisions.

Top Benefits of Completing a Diploma of Business
2. Expands Career Opportunities
One of the primary benefits of completing a Diploma of Business is the vast array of career opportunities that it opens up. This qualification is highly regarded by employers, particularly those in management, administration, and leadership roles. Many people who complete the diploma go on to work in fields such as marketing, project management, human resources, business development, and sales. With the right set of skills, individuals can pursue positions such as:
Business Manager
Operations Manager
Project Coordinator
Human Resources Officer
Marketing Coordinator
Sales Manager
Additionally, for those who are already employed, obtaining a Diploma of Business may help pave the way for career advancement within their current organization. https://aimsinstitute.edu.au/fees-and-refund-policy/
Advancement Opportunities
Completing the diploma may lead to promotions or internal transfers to higher-level roles. For example, someone working as an administrative assistant could progress into a management or operations role. By gaining more specialized knowledge, individuals become more valuable to their employer, which increases their chances of moving into senior roles.
3. Provides Flexibility and Versatility
Another great benefit of a Diploma of Business is its versatility. The skills and knowledge gained can be applied to various industries and organizations, ranging from small startups to large corporations. The business principles taught in this program are universal and can be adapted to almost any career path, which makes the qualification highly flexible. Whether you’re working in retail, healthcare, hospitality, or finance, the principles of business management, marketing, and operations are relevant.
Industry Applicability
Retail and Sales: Understanding customer needs and optimizing sales strategies are crucial for success in retail.
Healthcare: The business knowledge gained can help manage healthcare facilities, ensuring efficient operations and patient satisfaction.
Technology and Startups: The business principles learned can help launch and grow new businesses in the ever-evolving tech industry.
Hospitality: With a focus on management, marketing, and customer service, the diploma can help individuals excel in the hospitality and tourism sectors.
4. Affordable and Time-Efficient
The Diploma of Business is an affordable alternative to a full bachelor’s degree. For those looking to break into the business world quickly, completing a diploma program can be a time-efficient and cost-effective solution. Most diploma programs can be completed in one to two years, depending on whether you choose a full-time or part-time study option. For many students, this makes the diploma a more accessible choice compared to longer and more expensive degree programs.
Moreover, diploma courses often offer flexible study options, such as online learning or evening classes, which makes it easier for individuals to balance their education with work or family commitments.
Cost-Effective Education
The diploma offers a high return on investment, as it provides practical skills that can be applied immediately in the workforce.
Lower tuition fees compared to degree programs make the diploma more affordable for many students.
Financial aid or payment plans may be available to ease the financial burden of tuition.
5. Builds a Strong Network
Completing a Diploma of Business can also help build valuable professional networks. Throughout the course, students are likely to interact with peers, industry professionals, and instructors, which provides numerous opportunities to form meaningful connections. Networking with fellow students, especially those with different professional backgrounds, can offer new perspectives and business ideas. Furthermore, the connections made during the program may help with future job opportunities, internships, or collaborative business ventures.
Networking Opportunities
Industry Events and Seminars: Many diploma programs offer networking events, workshops, or guest speaker sessions that allow students to connect with industry leaders.
Alumni Networks: Graduates of business programs often join alumni networks, which can be valuable for career advice, job referrals, and mentorship.
Internships and Work Experience: Some programs may also offer internship opportunities, providing direct experience in the field and a chance to network with potential employers. Find our brochure here.
6. Enhances Entrepreneurial Skills
For those interested in starting their own business, a Diploma of Business can provide essential knowledge and skills to launch a successful entrepreneurial venture. Students are taught critical skills such as business planning, financial management, marketing strategies, and leadership. These areas of expertise are essential for anyone looking to run a business or manage a startup. The diploma program equips aspiring entrepreneurs with the confidence and know-how to take on the challenges of running a business in today’s competitive marketplace.
Essential Entrepreneurial Skills
Business Planning: Understanding how to create a business plan, set goals, and define strategies for success.
Financial Management: Learning how to manage cash flow, budget, and allocate resources effectively.
Marketing and Branding: Gaining skills to promote and grow a business in a crowded market.
Leadership: Knowing how to lead a team, build company culture, and inspire employees.
7. Supports Continuous Professional Development
Completing a Diploma of Business can be the starting point for a lifetime of continuous learning and career development. As business trends and technologies evolve, staying current is crucial. Many individuals who complete the diploma pursue further education, such as bachelor’s degrees, certifications, or specialized training, to advance their skills even further. The foundation provided by the diploma makes it easier to transition into higher levels of study or professional certifications.
Opportunities for Ongoing Learning
Bachelor’s Degrees: Some individuals use the diploma as a stepping stone to pursue a related bachelor’s degree in business or management.
Certifications and Workshops: Specialized certifications in areas like project management, digital marketing, or human resources can complement the diploma and expand career options.
Conclusion
The Diploma of Business is a highly beneficial qualification for anyone looking to advance their career, enhance their skill set, or break into the business world. From expanding career opportunities and building professional networks to gaining versatile, practical skills, the diploma offers numerous advantages. Its affordability, flexibility, and applicability across industries make it an attractive option for many students and professionals. Whether you’re aiming for a managerial position, pursuing entrepreneurship, or seeking career advancement, completing a Diploma of Business can provide a solid foundation for achieving your goals. https://www.usi.gov.au/students/get-a-usi
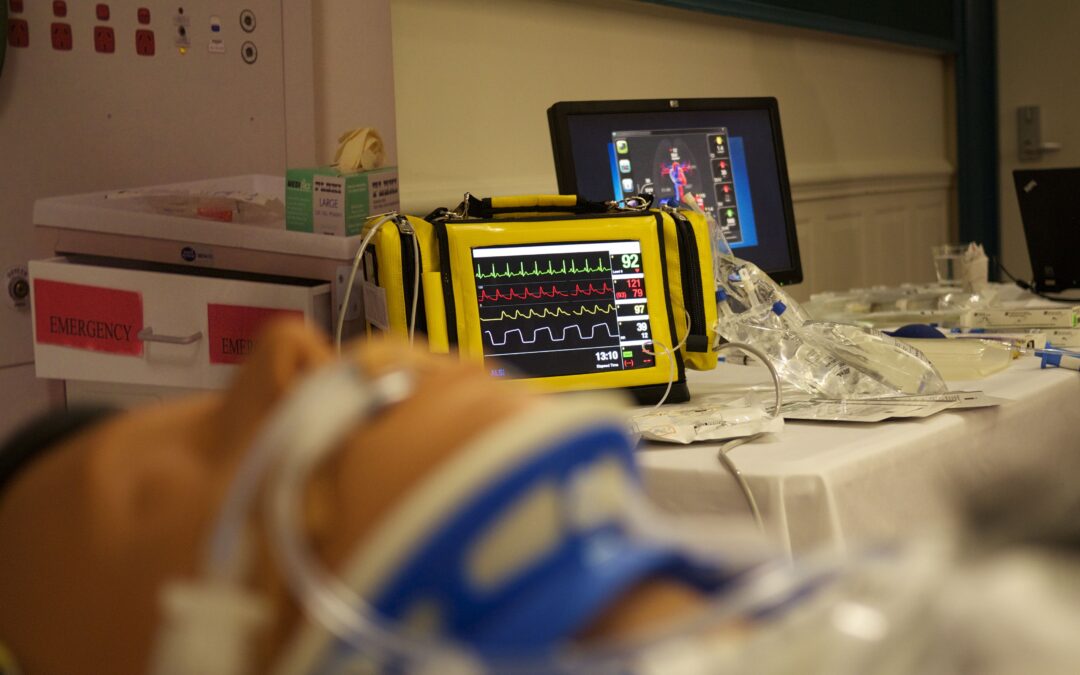
by admin | Nov 6, 2024 | blog
What Makes an Effective Life Support Course?
Introduction to Life Support Courses
Life support courses play a critical role in equipping individuals with the skills necessary to respond to emergencies effectively. These courses cover a variety of essential topics, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), first aid techniques, and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs). However, not all life support courses are created equal. Understanding the characteristics of an effective life support course can significantly enhance the learning experience and improve outcomes during real-life emergencies. This article delves into the key elements that make a life support course effective.
Key Characteristics of Effective Life Support Courses
1. Comprehensive Curriculum
An effective life support course should provide a comprehensive curriculum that covers all critical aspects of life support techniques. This includes not only CPR and AED training but also first aid procedures for various emergencies such as choking, bleeding, and trauma care. The curriculum should be designed to meet the needs of the target audience, whether they are healthcare professionals, teachers, or the general public. A well-rounded course ensures participants have the knowledge and skills necessary to respond confidently in a wide range of situations.
2. Experienced Instructors
The quality of instruction plays a vital role in the effectiveness of any training program. Effective life support courses are led by experienced instructors who possess a deep understanding of the material and practical experience in emergency situations. Instructors should be certified and regularly update their skills to reflect current best practices. Moreover, an effective instructor should be able to engage participants, answer questions, and provide constructive feedback, fostering an interactive learning environment that encourages participation and retention of information.
3. Hands-On Training
Theory alone is not enough to prepare individuals for real-life emergencies. Effective life support courses incorporate hands-on training to allow participants to practice skills in a safe environment. This includes using manikins for CPR practice, simulating emergency scenarios, and utilizing AEDs during training exercises. Hands-on training helps reinforce learning by allowing participants to apply their knowledge in realistic situations, building confidence and competence. The opportunity to practice skills repeatedly is essential for muscle memory, which is crucial during high-stress emergencies.
Utilization of Modern Technology
4. Incorporating Technology into Training
In today’s digital age, incorporating technology into life support courses can enhance the learning experience. Effective courses often utilize modern tools such as instructional videos, interactive online modules, and mobile applications to supplement traditional training methods. Virtual simulations and augmented reality can create immersive learning experiences that mimic real-life scenarios, helping participants prepare for the unexpected. Technology can also make training more accessible, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace and revisit materials as needed.
5. Regular Updates to Content
Emergency response guidelines and best practices evolve over time. An effective life support course regularly updates its content to reflect the latest research, techniques, and recommendations from recognized organizations such as the American Heart Association (AHA) and the Red Cross. Keeping course materials current ensures that participants receive relevant and accurate information, increasing their confidence in applying what they have learned in real-life situations. Instructors should also be trained to incorporate updates into their teaching, reinforcing the importance of ongoing education. Enrole here for a diploma of business
6. Comprehensive Assessment Methods

What Makes an Effective Life Support Course?
Assessment is a crucial component of an effective life support course. Participants should undergo both theoretical and practical assessments to demonstrate their understanding and application of the material. Effective courses use a variety of assessment methods, including written tests, skills checklists, and scenario-based evaluations. These assessments help identify areas where participants may need additional practice and ensure that they are competent in the skills required for emergency response.
7. Certification and Recognition
Certification is often the goal of participants in life support courses. An effective course should provide a recognized certification upon successful completion, which signifies that the individual has demonstrated competence in the necessary skills. This certification can be a valuable asset for professionals in fields such as healthcare, education, and emergency services. It is essential for the course to align with the requirements of relevant certifying bodies to ensure that the certification holds value in the workplace and enhances the participant’s credentials.
Community and Accessibility
8. Community-Focused Training
An effective life support course should be accessible to the community it serves. Offering training sessions in various locations, such as schools, community centers, and workplaces, can help reach a broader audience. Additionally, courses should consider the specific needs of the community, including language barriers and cultural differences. Providing courses at no or low cost can increase participation, ensuring that more individuals have the opportunity to learn essential life support skills. Engaging local organizations and businesses can also promote training initiatives and foster a sense of community involvement.
9. Ongoing Support and Resources
Effective life support courses do not end with the completion of the training. Providing ongoing support and resources helps participants reinforce their skills and stay informed about best practices. This can include access to refresher courses, online resources, and community workshops. Establishing a network of trained individuals can create a supportive environment where participants feel comfortable seeking guidance and sharing experiences. Ongoing engagement with alumni of the course can help maintain skills and encourage individuals to remain proactive in their emergency preparedness.
Feedback and Improvement
10. Importance of Feedback
An effective life support course actively seeks feedback from participants to improve the training experience continually. Surveys, focus groups, and one-on-one discussions can provide valuable insights into what worked well and what could be enhanced. Instructors should encourage open communication and be receptive to constructive criticism. This feedback loop helps course providers identify strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to adapt and refine their programs to better meet the needs of participants.
11. Continuous Improvement
The commitment to continuous improvement is a hallmark of effective life support courses. By regularly reviewing and updating course content, teaching methods, and assessment strategies based on participant feedback and evolving best practices, course providers can ensure they deliver high-quality training. Continuous improvement not only benefits participants but also enhances the reputation of the training organization, attracting more individuals to enroll in their programs.
Conclusion
Effective life support courses are essential in equipping individuals with the skills and confidence necessary to respond to emergencies. By focusing on a comprehensive curriculum, experienced instructors, hands-on training, and the integration of modern technology, these courses can significantly enhance the learning experience. Additionally, community-focused training, ongoing support, and a commitment to feedback and improvement further contribute to the effectiveness of life support courses. As we strive to create safer communities, investing in quality life support training will empower individuals to act decisively in critical situations, ultimately saving lives and fostering a culture of preparedness.










